Dwarf Meyer Tree: Care, Cultivation, and Benefits


Intro
The Dwarf Meyer tree is not just a smaller version of the Meyer lemon tree; it stands out with its notable charm and vigor. This compact variant has carved a niche in gardens and homes, becoming a favorite among those who wish to incorporate a tropical flair into a limited space. As we embark on this journey of understanding the Dwarf Meyer tree, we'll consider a variety of aspects that highlight why it deserves a place in every garden enthusiast's repertoire. From its growth patterns and requirements to the pests that might invade its vibrant leaves, we’ll explore all facets of this delightful tree.
Growing a Dwarf Meyer tree is like tending to a piece of art; it takes patience, knowledge, and care. Even as we dive into practical advice on cultivation techniques, we must not overlook its rich history and the cultural importance it has in different regions of the world. Whether you’re a seasoned horticulturist or a budding gardener, there’s something deeply rewarding about watching this tree flourish and provide fruit.
This guide seeks to illuminate the peculiarities and care methods that will help you nurture your very own Dwarf Meyer tree. Undoubtedly, this little tree packs a punch with its fragrant blossoms and juicy fruits, making it a true treasure in any garden.
Dwarf Meyer Tree Profile
General Overview
The Dwarf Meyer tree is a hybrid, likely a mix of true lemon and mandarin orange species. It usually reaches a height of about three to four feet, making it perfectly suitable for container gardening. The leaves are glossy and deep green, while the flowers are mildly fragrant, giving off a scent that is often described as sweet and citrusy. When it comes to fruit, expect lemons that are more rounded and somewhat sweeter than typical lemons. These small, juicy gems are a delightful addition to any dish, enhancing flavors and adding that special zing.
Habitat and Distribution
Originally, the Meyer lemon was first introduced to the United States from China in the early 20th century. Given its roots, the tree thrives best in warmer climates, but it can adapt well to various environments, especially when grown indoors or in a greenhouse. The ideal temperature range for this tree is between 70 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit during the day. However, it can withstand cooler temperatures down to 30 degrees Fahrenheit if necessary, making it a versatile choice for a wide range of environments.
Fascinating Facts
Unique Traits and Adaptations
The Dwarf Meyer tree is known for more than just its size and taste. One of its most interesting traits is its ability to be grown in pots, allowing for mobility and flexibility in care. During the warmer months, it can be moved outdoors to soak up sunlight, and in winter, it can be brought inside to protect it from frost. Furthermore, its resilience against certain diseases makes it a popular choice among home gardeners.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Historically, the Meyer lemon has played a role in American gardening culture, particularly in Californian landscapes. It's often associated with home gardens and small orchards. Many gardeners embrace the tree not only for its practical benefits but also for its nostalgic value—recalling family gatherings and homemade lemonade during summer picnics.
Conservation Status
Current Population Trends
While the Dwarf Meyer tree isn't classified as endangered, its popularity has indeed grown among gardeners. This increased interest might lead to cultivation practices that can either benefit or threaten its existence in specific regions. Sustainable methods of care can enhance its presence in artisanal gardens.
Threats and Challenges
Despite its robust nature, the Dwarf Meyer tree faces challenges, primarily from pests and diseases. Aphids, spider mites, and scale insects are common nuisances that can detract from its health and fruiting potential. Moreover, overwatering or poor drainage can lead to root rot, affecting its longevity. Keeping a vigilant eye on your tree can help mitigate these threats and ensure a healthy yield.
Care Tips for Gardeners
Basic Needs and Requirements
The Dwarf Meyer tree enjoys full sun, so planting it in a location that receives at least six to eight hours of direct sunlight is crucial. Soil should be well-draining, with a mix of potting soil and sand or perlite for optimal results.
Health and Wellness Tips
- Regular Pruning: This encourages new growth and helps maintain shape.
- Fertilization: Use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer during the growing season.
- Watering: Keep the soil slightly moist but never waterlogged. Adjust watering depending on the season and the plant's growth phase.
- Pest Monitoring: Inspect the tree regularly for signs of pests and treat promptly with organic methods whenever possible to ensure safety.
Prolusion to the Dwarf Meyer Tree
The Dwarf Meyer tree is more than just a plant; it's a conversation starter in gardens and a treasure for those who enjoy unique flavors. Its charm lies not only in its ability to bear fruit but also in the delightful, aromatic presence it adds to any space. Understanding this tree involves diving into its historical journey, its botanical background, and the reasons why it deserves a spot in your garden.
When considering the inclusion of the Dwarf Meyer tree in an orchard or landscape, one should reflect on its versatility, compact size, and ability to thrive in varied conditions. These characteristics present advantages that appeal to both seasoned horticulturists and casual cultivators. For instance, its smaller stature allows for its growth in pots, making it ideal for balconies and patios. Moreover, the fruit's compatibility with a multitude of culinary applications adds a layer of functionality.
Historical Context
The Dwarf Meyer tree has an intriguing past that dates back to the early 20th century. Originally, this tree is believed to have been brought from China, where it was cultivated for generations. The tree’s association with the well-known horticulturist Frank Meyer is where it got its name. Meyer undertook his journeys across the globe in search of rare plants. Upon discovering this particular variety in the 1900s, he introduced it to the United States, where it captured the interest of many. Its introduction was pivotal; this was a time when gardeners were eager to approach citrus cultivation with new varieties that promised flavor and adaptability.
As it garnered popularity, the Dwarf Meyer tree became a staple in home gardens and commercial orchards, particularly in regions with temperate climates. The historical narrative of this tree is a testimony to human curiosity and the desire to expand the realm of what is possible in gardening.
Botanical Classification
To fully appreciate the Dwarf Meyer tree, understanding its botanical classification is essential. Scientifically known as Citrus × meyeri, this tree is a hybrid. It emerges from the crossover between a true lemon (Citrus limon) and a mandarin orange (Citrus reticulata). The distinctive characteristics that arise from this hybridization are particularly fascinating, blending the tartness of lemons with the sweetness of mandarins.
In terms of growth habits, the Dwarf Meyer tree typically reaches a height of about three to four feet when kept in a pot and can grow somewhat larger in the ground. The leaves are dark green, glossy, and arise from thick branches that provide a robust structure. This tree’s classification isn’t solely about its lineage; it embodies a blend of taste and visual appeal, making it a valuable addition to any garden aesthetic.
Understanding both the historical journey and botanical relationships of the Dwarf Meyer tree enriches our appreciation and encourages a deeper engagement with this remarkable plant. Its resilience and adaptability open avenues for diverse planting methods and gardening styles.
Physical Characteristics
The physical characteristics of the Dwarf Meyer tree play a crucial role not only in its aesthetic appeal but also in its growth habits and environmental adaptability. Understanding these characteristics helps gardeners make informed decisions about cultivation and care. By recognizing elements such as size, shape, leaves, flowers, and fruits, one can better appreciate the uniqueness of this tree, thereby enhancing gardening practices and ensuring successful growth.
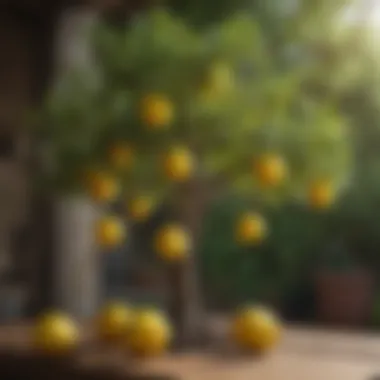

Size and Shape
The Dwarf Meyer tree is notably compact, typically reaching about 3 to 4 feet in height. This is a stark contrast to the standard Meyer lemon tree, which can tower over 6 feet. The managed size of the Dwarf Meyer allows it to thrive in smaller gardens and even pots, making it an excellent choice for urban spaces. Its rounded shape adds a unique flair to any landscape, giving it both ornamental and practical uses.
The tree’s branching structure is dense, forming a lush canopy that offers shade while maintaining an airy feel. This characteristic not only looks pleasing but also optimizes sunlight capture for photosynthesis. Gardeners can easily maintain its size through pruning, which further enhances its bushy appearance, promoting more flowers and fruit development.
Leaves and Flowers
The Dwarf Meyer tree boasts glossy, deep green leaves that are broad and oval-shaped. These leaves are not just visually appealing; they also release a delightful fragrance when brushed against, adding a sensory experience to any garden. Their thickness is indicative of their health, providing resilience against pests and diseases.
When it comes to flowers, this tree is a true showstopper. The blooms emerge in clusters and are usually white with a hint of lavender, exuding a sweet scent that attracts pollinators such as bees. Each flower is relatively small, but they pack a visual punch, creating a beautiful display that can turn heads. The flowering period is typically in early spring, although, with mild conditions, blooms can occur at various times throughout the year. This continual blooming can enhance a garden's aesthetic throughout multiple seasons.
Fruit Description
One of the appealing features of the Dwarf Meyer tree is its fruit. The lemons produced are smaller, usually about the size of a golf ball, and are known for their bright yellow skin and slightly rounder shape compared to their larger counterparts. The skin is thinner, which means a juicier fruit inside. The taste is something to rave about; it has a sweeter flavor than standard lemons with a rich, aromatic profile that makes it ideal for culinary uses.
Each fruit contains numerous seeds, although the tree can also produce seedless varieties, depending on the cultivator's practices. When fully ripe, the fruits not only provide a delightful treat but also add a vibrant splash of color to the tree, creating a picturesque scene right in your backyard.
"Growing a Dwarf Meyer tree means more than cultivating a plant; it’s about enriching your home with flavors and scents that evoke warmth and relaxation."
In summary, the physical characteristics of the Dwarf Meyer tree are not merely functional; they offer a rich backdrop for any gardener seeking to make a statement. From the compact size to the fragrant flowers and juicy fruits, every aspect contributes to both its beauty and its practical utility in culinary applications.
Cultivation Requirements
When it comes to nurturing the Dwarf Meyer tree, understanding its cultivation requirements is crucial for achieving a thriving and fruitful plant. This section dives into the essentials, including soil preferences, light conditions, and watering practices. Mastering these elements can not only promote healthy growth but also ensure better yields and resilience against pests and diseases.
Soil Preferences
Dwarf Meyer trees prefer well-draining soil that retains some moisture without becoming soggy. A sandy loam or a mix that incorporates organic matter is ideal. This kind of soil provides the right balance of nutrients, aeration, and drainage. Here are some specific types of soil that work well for cultivating these trees:
- Citrus-specific blends: Many garden centers offer potting mixes tailored for citrus trees, enhancing growth.
- Custom blends: Mixing equal parts peat moss, perlite, and topsoil can create a home-friendly environment for your Dwarf Meyer tree.
It’s important to avoid heavy clay soils that can hold water, causing root rot. Before planting, testing the soil pH can also be beneficial, as Dwarf Meyer trees thrive best in slightly acidic to neutral pH levels ranging from 5.5 to 6.5.
Light Conditions
Adequate sunlight is non-negotiable for the Dwarf Meyer tree. Ideally, these trees need full sun, which means around 8 to 10 hours of direct sunlight each day. Here’s how to ensure your tree gets the right amount of light:
- Placement: If you’re planting it outdoors, position the tree where it can bask in morning sun, but be wary of harsh afternoon rays in hotter regions. If the tree is indoors, a south-facing window is preferable.
- Light quality: The quality matters too. Fluorescent or LED grow lights can supplement natural light during shorter days or gloomy weather.
Insufficient light can hinder the development of flowers and fruits, leading to disappointment when harvest time rolls around.
Watering Practices
Effective watering is foundational for maintaining the health of a Dwarf Meyer tree. The general rule of thumb is that young trees require more frequent watering than established ones. Here are some key guidelines to follow:
- Frequency: Water deeply but infrequently. Aim for a schedule that allows the top two inches of soil to dry out between watering.
- Methods: Use drip irrigation or a soaker hose to deliver moisture directly to the roots. Avoid overhead watering to reduce the chances of fungal diseases.
- Signs of distress: Pay attention to how your tree reacts to watering. Leaves that turn yellow might indicate overwatering, while a droopy appearance could signal underwatering.
By adhering to specific soil, light, and water requirements, your Dwarf Meyer tree can flourish, bringing both beauty and bounty to your space.
Propagation Techniques
Propagation techniques are the cornerstone of successfully cultivating the Dwarf Meyer tree. This process not only enhances the sustainability of the tree itself but also allows gardeners to produce new plants that mirror the qualities of the parent tree. Understanding these methods can give gardeners greater control over their cultivation efforts and contribute to more fruitful and robust plants over time.
Seed Propagation
Seed propagation involves cultivating plants from seeds harvested from mature Dwarf Meyer trees. This method might seem straightforward, but it comes with its own set of challenges. For one, seeds from hybrid plants like the Dwarf Meyer can sometimes produce offspring that don't resemble the parent tree, making this method a gamble in terms of quality. However, this technique is often chosen for its educational value and the experience it provides. When starting from seeds, gardeners should follow these steps:
- Seed Selection: Choose seeds that have been properly harvested from fully ripe fruits. The freshness and viability of the seeds significantly influence their ability to germinate.
- Preparing Seeds: Before planting, clean and dry the seeds for a couple of days. This helps prevent mold and ensures optimal growth.
- Planting: Plant the seeds in a well-draining potting mix. Cover them lightly with soil and keep them moist but not soggy.
- Germination: Place the pots in a warm, illuminated area. Ideally, temperatures around 70°F to 75°F will promote faster germination.
While seed propagation can be a slow process, requiring patience and consistent care, it is also a rewarding experience for those looking to familiarize themselves with the growth habits of the Dwarf Meyer tree firsthand.
Cuttings and Grafting
Cuttings and grafting present more reliable methods for propagating the Dwarf Meyer tree. These techniques allow gardeners to create new trees with the exact genetic makeup of the parent plant, which is particularly significant for those growing for commercial purposes or specific desired traits.
Cuttings
Cuttings involve taking a portion of a healthy tree, usually a branch or twig, and encouraging it to root and form a new plant. For success in this method, it's advisable to follow these steps:
- Choosing the Right Cutting: Select a semi-hardwood cutting that measures around 4-6 inches long, just behind a node, where leaves emerge.
- Preparing the Cutting: Remove the lower leaves while leaving a couple of leaves at the top. This helps reduce moisture loss.
- Rooting Hormone: Dipping the cut end in rooting hormone can significantly boost the chances of successful rooting, although it's not strictly necessary.
- Planting: Insert the cutting into a small pot filled with a suitable potting mix and water it lightly.
- Environment: Create a greenhouse effect by covering the pot with a clear plastic bag or a glass jar, ensuring there is some ventilation to prevent mold.


Grafting
Grafting, on the other hand, involves joining parts of two plants together so they grow as one. This technique is usually used to combine the best traits of both the rootstock and the scion (the upper part). Here’s a simplified approach to grafting Dwarf Meyer trees:
- Selecting Scion and Rootstock: Choose healthy, compatible plants — the rootstock should be vigorous, and the scion should come from a healthy Dwarf Meyer tree.
- Making the Cuts: A clean cut is essential. Make a slanting cut on the scion and a matching cut on the rootstock.
- Joining and Wrapping: Align the cambium layers of both pieces, then wrap them together securely with grafting tape to prevent moisture loss.
- Aftercare: Keep the grafted plant in a sheltered area and monitor for signs of growth, usually visible in a few weeks.
Both cuttings and grafting provide more precise control over the characteristics of new trees and maximize yield potential while preserving the unique traits inherent in the Dwarf Meyer tree. By mastering these propagation techniques, gardeners can ensure a sustainable and productive approach to growing these delightful trees.
"The art of propagation not only fulfills our gardening ambitions but also enriches our connection to nature and its cycles." - Unknown
Pest and Disease Management
Effective pest and disease management is crucial when caring for the Dwarf Meyer tree. Keeping these botanical wonders healthy not only maximizes their growth potential but also ensures the delight of their fragrance and fruit. When issues arise, they can quickly turn your thriving little tree into a sad sight. This section will delve into the common pests that threaten the Dwarf Meyer, how to prevent infestations, and the treatment options available for when management strategies fall short.
Common Pests
Dwarf Meyer trees, like many plants, can be susceptible to a variety of pests. Some of the most persistent nuisances include:
- Aphids: These tiny, soft-bodied insects often cluster on new growth and tender leaves. They suck the tree sap, weakening the plant and potentially causing leaf curl.
- Spider Mites: Difficult to spot at first glance, spider mites create fine webbing on the leaves. They thrive in dry conditions and can lead to stippling on leaves, making them look sickly and discolored.
- Scale Insects: These pests resemble little bumps on twigs and leaves. They can be hard to detect but can drain the vigor of the tree.
- Leaf Miners: These larvae tunnel through leaves, creating unsightly trails that can impact photosynthesis.
These pests not only hurt the tree’s overall health but can also open the door for diseases to take hold.
Preventive Measures
Taking a proactive approach to pest management can make a world of difference. Here are some effective preventive measures:
- Regular Monitoring: Often, early detection is the best defense. Check your tree regularly for any signs of pests or unusual changes in foliage.
- Proper Pruning: Keeping your Dwarf Meyer tree well-shaped and ventilated allows for good air circulation, reducing humidity that can attract pests.
- Healthy Soil: A well-balanced, nutrient-rich soil promotes strong, resilient plants. A solid foundation can fend off many health issues.
- Natural Predators: Introducing beneficial insects, like ladybugs and lacewings, can help keep pest populations in check.
- Organic Insecticides: Neem oil or insecticidal soaps can deter pests without harming the tree or surrounding environment.
Treatment Options
Should pests find their way onto your Dwarf Meyer, it's vital to act swiftly. Here are some options:
- Manual Removal: For visible pests like aphids or scale, a simple spray of water can dislodge them. A soft cloth can help wipe off any that cling stubbornly.
- Insecticidal Soaps: These can be effective for soft-bodied insects and generally are safe for plants when used as directed.
- Horticultural Oils: These oils can smother pests, particularly effective against scale insects and spider mites when carefully applied.
- Systemic Insecticides: In cases of severe infestation, systemic insecticides may be needed. Be cautious, as these can also affect beneficial insects.
Proper pest management not only preserves the Dwarf Meyer tree's health but enhances the quality and quantity of its yields. Taking action early can save a lot of trouble later.
Navigating the challenges of pest and disease management takes diligence and knowledge. By being educated about common foes and implementing preventive strategies, gardeners can create a thriving environment where the Dwarf Meyer tree can flourish.
Harvesting and Usage
The act of harvesting the Dwarf Meyer tree holds significant importance, as it not only affects the tree's health but also directly impacts the culinary potential and nutritional benefits of its fruit. Understanding the best techniques and timings for harvesting can optimize not just yield but also flavor and quality of the fruit, making this an essential topic for anyone cultivating this delightful addition to their garden. The fruits of the Dwarf Meyer tree are a crossover delight between a lemon and an orange, often richer in zest and juice, which brings about the need for a thoughtful approach to harvesting and subsequent usage.
Optimal Harvesting Time
When it comes to the Dwarf Meyer tree, timing is crucial. The best moment to harvest typically falls about 6 to 9 months after flowering. The fruit changes color from a bright green to a vibrant yellow-orange, signaling its readiness. However, it’s not just about color – give it a gentle squeeze. If it feels slightly soft, it’s often perfect for picking. One key thing to remember is that fruit doesn't continue to ripen significantly once picked, a common misconception with citrus.
Some gardeners make a habit of checking their trees every few days, particularly as summer heat kicks in. This constant observation can help catch the ripe fruit at just the right moment, ensuring maximum juiciness and flavor.
Culinary Applications
The culinary versatility of the Dwarf Meyer tree's fruit is one of its standout features. Given its sweeter flavor profile compared to traditional lemons, the fruit is highly sought after in various recipes. You might enjoy it in desserts, such as cakes or tarts, or use its juice to enhance marinades or salad dressings. Its zest can elevate various dishes, providing that citrus punch without the overpowering tartness of regular lemons.
- Meyer Lemon Bars: A twist on the traditional lemon bar, using the Dwarf Meyer variation for a softer flavor.
- Salad Dressings: Combine juice and olive oil for a fresh dressing that can brighten any salad.
- Cocktails: The added sweetness makes it a favorite for mixed drinks, from refreshing lemonades to sophisticated cocktails.
And, let’s not overlook the trend of using Meyer lemons in preserving, whether in marmalades or pickles, enhancing both taste and texture.
Nutritional Benefits
Besides its culinary charm, the Dwarf Meyer tree’s fruit carries a payload of nutritional perks. These fruits are rich in vitamin C, providing immune system support and enhancing skin health. Let’s consider the specifics:
"One medium Meyer lemon contains about 31 mg of Vitamin C, which is approximately 34% of the daily recommended intake."
In addition to Vitamin C, these lemons also contribute small amounts of potassium, calcium, and magnesium, which can aid in muscle function and electrolyte balance. Here are some noteworthy benefits:
- Antioxidant properties: Helps combat oxidative stress in the body.
- Weight Management: Low in calories but high in flavor, making them an excellent choice for various diets.
In sum, the Dwarf Meyer tree's contribution to gastronomy and health is substantial. Knowing the best times to harvest, how to utilize its fruit in cooking, and appreciating its nutritional benefits can enrich both your garden and your plate.
Landscaping with the Dwarf Meyer Tree
When it comes to enhancing a garden, few plants can bring the aesthetic and functional beauty of the Dwarf Meyer tree to the fore. This small citrus tree not only serves as a delightful addition to any landscape but also offers a myriad of benefits to both the garden and the gardener. It thrives in various settings and can elevate the charm of your outdoor space with its lush foliage and aromatic fruit.

Complementing Other Plants
The Dwarf Meyer tree can be a wonderful companion to a variety of plants in your landscape. Given its moderate height, typically topping out around three to four feet, it's an ideal candidate for smaller gardens or patios.
Here’s how it can complement other plants:
- Color Contrast: The rich green leaves and yellow flowers provide a striking contrast to darker foliage like Loropetalum or Japanese Maple. Bright fruits against green leaves can create a visually stunning narrative in your garden.
- Fragrant Mix: The sweet, citrusy fragrance of the Dwarf Meyer flowers pairs delightful with aromatic herbs such as basil, mint, or even rosemary. These scents create an inviting atmosphere that can make your outdoor space a sanctuary.
- Layering: When planted alongside taller plants, like pines or redwoods, the Dwarf Meyer tree can add depth to the landscape. Its rounded shape provides a softness, contrasting the linear textures of taller plants.
- Edible Landscape: Integrating the Dwarf Meyer tree into your edible garden not only enhances beauty but provides fresh lemons for culinary uses. Its fruit can be harvested right off the tree, adding convenience to your cooking.
Seasonal Considerations
Landscaping with the Dwarf Meyer tree also requires an understanding of seasonal changes, allowing optimal growth and aesthetics throughout the year. The tree has a few key characteristics that make it suitable for various seasons:
- Spring Growth: In spring, the Dwarf Meyer tree bursts into bloom with fragrant white flowers. This is the time to highlight it in your garden, given its attractive blooms that draw pollinators like bees.
- Summer Bounty: As summer hits, watch as your Dwarf Meyer tree dazzles with bright green leaves and budding fruits. Consider pairing it with summer-blooming perennials like coneflowers or lavender, creating a lively display.
- Fall Harvest: Fall marks a significant period as the fruits ripen. It's crucial for gardeners to harvest at the right time, ensuring the best flavor. This is also an excellent time to showcase their fruits in decorative arrangements.
- Winter Resilience: In winter, while the tree may lose leaves, its structured form can still provide aesthetic value. Consider decorating it with fairy lights for a festive touch, making your garden glow during the frosty nights.
Incorporating the Dwarf Meyer tree into your landscape offers not only visual appeal but also enriches the gardening experience. Its versatility in complementing other plants and adapting beautifully to seasonal rhythms makes it a compelling choice for enhancing any garden.
Cultural Significance
The cultural importance of the Dwarf Meyer tree goes beyond its horticultural appeal. This tree not only adds beauty and flavor to gardens but also enriches various cuisines and symbolizes broader themes in different cultures. Delving into its role provides insight into how the Dwarf Meyer tree has intertwined itself within culinary and social frameworks.
In Culinary Traditions
The Dwarf Meyer tree is often hailed in culinary circles for its unique fruit, which introduces a delicate sweetness rarely found in traditional lemons. This feature significantly influences its role in various dishes. For instance, its zest is prized for brightening flavors in both savory and sweet dishes. Imagine a rich risotto slowly infused with Meyer lemon juice or a delicate lemon meringue pie chatoyant with vibrant zest. Recipes like these transform simple meals into culinary experiences, seeking to impress guests or family alike.
- Use in Beverages: The Dwarf Meyer tree has earned a niche place in mixology. Bartenders incorporate its juice into cocktails, making refreshing drinks that are a crowd-pleaser. A classic Meyer lemon martini boasts a tangy yet sweet kick that’s hard to resist on a warm day.
- Culinary Versatility: Beyond main courses, the Meyer lemon's mild flavor extends to salad dressings, marinades, and even desserts. Its adaptability is one reason it holds such esteem in kitchens around the world.
The cultivation of this tree overlaps with culinary heritage, as families often pass down beloved recipes featuring its fruit.
Symbolism in Different Cultures
In many cultures, the Dwarf Meyer tree isn’t just a source of food; it represents fertility, prosperity, and even protection. In societies where the tree thrives, gifting one is a gesture of goodwill and hope. The presence of the tree in a home garden can evoke a sense of happiness and family unity.
- East Asian Traditions: In places like China and Japan, citrus trees, including the Meyer lemon, symbolize abundance and good fortune. These connections often find manifestation during celebrations like Lunar New Year, where lemon trees are a common decoration.
- Folklore and Mythology: Various tales have emerged around lemon trees. Some say the vibrant color wards off negative energy, while others claim it brings light into the home. These interpretations enrich the cultural footprint of the tree, making it more than just an ornamental plant.
As the Dwarf Meyer tree permeates culinary practices and cultural beliefs, it serves as a reminder of how nature can blend seamlessly into human experiences, enriching lives through both physical and metaphorical nourishment.
As one tends to the Dwarf Meyer tree, they engage with a legacy of flavors and meanings, connecting past with present and enriching our cultural landscape.
Conservation and Environmental Impact
Understanding the conservation and environmental impact of the Dwarf Meyer tree goes beyond just its aesthetic appeal in gardens. This tree plays a pivotal role in promoting biodiversity and supporting ecological health. Among horticultural communities, there's growing recognition of the need to include flora that not only beautifies living spaces but also nurtures the environment. The Dwarf Meyer tree, due to its compact size and unique characteristics, proves to be an exemplary candidate in this regard.
To illustrate its contributions:
- Carbon Sequestration: Like all trees, the Dwarf Meyer contributes to capturing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping mitigate the effects of climate change. Its ability to thrive in diverse environments enables it to grow in a variety of urban landscapes, thereby addressing the increasing urban heat issue.
- Microclimate Creation: Planting Dwarf Meyer trees can create a favorable microclimate. These trees provide shade and help to reduce temperatures in their immediate vicinity, making them a beneficial addition to urban environments with heat islands.
- Aesthetic and Psychological Benefits: The presence of greenery, including the Dwarf Meyer tree, has been linked to improved mental well-being. Gardens that include these trees offer a serene atmosphere that encourages relaxation and promotes overall happiness.
While the Dwarf Meyer tree has numerous benefits, it is essential to consider certain factors to leverage its full potential.
Sustainable Practices
Implementing sustainable practices when cultivating the Dwarf Meyer tree is vital. These practices not only enhance the longevity of the tree but also ensure minimal negative impact on the environment.
- Organic Fertilizers: Utilizing organic fertilizers, such as compost or well-rotted manure, provides essential nutrients while reducing chemical runoff that could harm nearby ecosystems.
- Water Conservation: Employing efficient watering techniques such as drip irrigation can minimize water waste. The Dwarf Meyer tree’s resilience allows it to withstand brief periods of drought, making it particularly suited for water-efficient gardening.
- Integrated Pest Management: Adopting integrated pest management strategies helps address pest issues without relying heavily on chemical pesticides. Encouraging natural predators, such as ladybugs and lacewings, can promote a healthier, balanced garden ecosystem.
These sustainable approaches not only enhance the growth of the Dwarf Meyer but also encourage harmonious coexistence with the surrounding environment.
Supporting Local Ecosystems
The Dwarf Meyer tree holds significant potential to support local ecosystems in various ways. As it grows, it can contribute to the overall ecological balance.
- Attracting Pollinators: The fragrant flowers of the Dwarf Meyer tree attract various pollinators like bees and butterflies. This is crucial as pollinators play a critical role in maintaining plant diversity and ensuring the production of fruits and seeds across ecosystems.
- Habitat for Wildlife: The foliage and branches of these trees provide food and shelter for birds and insects, thereby fostering a more diverse and balanced wildlife population.
- Soil Health Improvement: The root system of the Dwarf Meyer tree can help in preventing soil erosion. Additionally, the leaves that fall from the tree decompose and enrich the soil, thus enhancing its nutrient composition.
In summary, recognizing the conservation and environmental impact of the Dwarf Meyer tree offers a multi-faceted lens through which to understand its place in contemporary gardening. Not only does it provide aesthetic and culinary value, but it also fosters a healthier ecosystem, making it a worthy addition to any garden.
Closure
As we draw the curtain on our exploration of the Dwarf Meyer tree, it's clear that this unique horticultural specimen holds a blend of charm and utility that captivates both novice and seasoned gardeners. From its rich history and distinctive botanical traits to its multitude of benefits in both culinary and environmental contexts, the Dwarf Meyer tree proves itself to be more than just a decorative addition to gardens.
Looking closely at its gardening potential, several factors emerge, all of which underline its growing appeal. First and foremost, the cultivation requirements are relatively manageable. This tree flourishes in various environments, allowing gardeners to enjoy its presence regardless of their climate zone. The pivotal criteria of soil, sunlight, and watering aren't overly demanding, making it an excellent choice for those still finding their footing in the world of gardening.
Moreover, the culinary applications of the Dwarf Meyer tree further solidify its importance. The fruit's delightful balance of sweet and tart flavors opens the door to a variety of culinary uses, from desserts to savory dishes. It enriches meals in ways that go beyond taste, injecting a bit of zest into both the homemade and professional kitchen.
The tree's role doesn't just stop at personal benefits. In a broader context, it contributes significantly to local ecosystems. With the right care, Dwarf Meyer trees can become habitats for various insects and birds, creating a vibrant micro-environment that promotes biodiversity.
In synthesizing all of these elements, it becomes evident that understanding this tree is just the beginning. The future potential of the Dwarf Meyer tree in gardening holds promise. Its adaptability, flavorful fruits, and ecological benefits align with the growing trend of sustainable and productive home gardening. The tree beckons gardeners to not just plant but to engage with it as a living entity that fosters growth and food security in our lives.
Navigating the nuances of this tree not only adds to our knowledge base but also enriches our gardens, kitchens, and communities, forging deeper connections with nature and our culinary heritage.















