Understanding Mite Bites on Human Skin: Identification and Implications

Intro
Mites, though small in size, can provoke significant reactions when they bite human skin. Understanding the implications of mite bites is essential due to their similarity to other skin irritations. This understanding enables proper identification and appropriate response to mitigate discomfort. This section sheds light on the characteristics of mite bites, their progression, and the necessary steps to address them.
Animal Profile
General Overview
Mites belong to the class Arachnida, a diverse group that includes spiders and ticks. They are often overlooked due to their minuscule size, typically measuring less than one millimeter. Common types of mites that bite humans include Sarcoptes scabiei, which causes scabies, and Demodex mites, which are part of normal skin flora but can cause skin issues in some individuals. Recognizing these species is pivotal for diagnosing and treating bites effectively.
Habitat and Distribution
Mites inhabit a range of environments. They can be found in both urban and rural settings, often residing in dust, soil, decaying plant matter, and even in animal fur. Environmental conditions, such as humidity and temperature, play a significant role in their lifecycle and distribution. Hot, humid areas tend to harbor higher populations of mites, increasing the risk of bites to humans.
Identifying Mite Bites
It is imperative to recognize the distinctive features of mite bites to differentiate them from other skin conditions. Mite bites may present as:
- Red, itchy welts
- Small, raised bumps
- Linear streaks in some cases, especially in scabies
Symptoms can vary depending on the individual's sensitivity and the type of mite involved. Itching is often a primary indicator, resulting from the body’s reaction to the saliva introduced during the bite.
Potential Complications
While many mite bites result in mild reactions, complications can arise, particularly if an infection occurs due to scratching. Secondary bacterial infections can lead to more severe skin conditions requiring medical attention. Severe allergic reactions are also possible but rare. It is advisable to seek professional help if symptoms worsen or do not resolve within a reasonable timeframe.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Identifying the source of mite bites requires a careful examination of the affected area and possibly the surrounding environment. A healthcare provider may utilize:
- Skin scrapings
- Clinical examination
- Patient history to determine exposure
Treatment often includes topical or oral medications, such as antihistamines for itching and topical corticosteroids for inflammation. In cases of scabies, specific medications like permethrin cream are typically recommended.
Preventive Measures
To minimize the risk of mite bites, consider the following measures:
- Maintain cleanliness in living spaces
- Regularly wash bedding and clothing in hot water
- Control humidity levels to discourage mite proliferation
- Use insect repellents in habitats known for high mite activity
Prolusion to Mite Bites
Mite bites can pose a significant concern for many individuals. Understanding the characteristics and implications of mite bites is essential not only for effective treatment but also for prevention. Identifying these bites can be especially challenging as they often resemble other skin irritations. Therefore, a focused discussion on this topic can help individuals discern between various conditions and take appropriate actions.
Overview of Mites
Mites are tiny arthropods belonging to the class Arachnida. These creatures vary in size, shape, and species, with some being harmless while others can cause considerable discomfort. Mites usually inhabit various environments, including homes, gardens, and wildlife areas. There are numerous species, but only a select few are known to bite humans. For instance, scabies mites, chigger mites, and bird mites are noteworthy due to their interactions with people.
Mites feed on various organic materials, including skin cells, which can lead to irritations or bites. The identification of different mites often requires careful observation and, in some cases, expert examination. Their life cycle phases include egg, larva, nymph, and adult stages, which can all play a role in their potential impact on human health. Ensuring we understand mites allows us to address infestations effectively and minimize health risks associated with these pests.
The Nightmares of Mite Infestations
Mite infestations are often overlooked, yet they can lead to substantial discomfort and health concerns. Infestations can result from poor hygiene, close contact with infested animals, or living in unsanitary conditions. The most notorious among these is the scabies mite. When they invade human skin, they burrow in, leading to severe itching and rash.
For many, the nightmares of mite infestations stem from the constant discomfort and psychological distress caused by itching and skin irritation. The embarrassment and anxiety surrounding visible rashes can create social challenges for affected individuals. Beyond physical symptoms, these infestations may also lead to secondary infections, further complicating treatment. Addressing these concerns early is crucial.
In summary, understanding mite bites is essential for proper identification and effective management. Knowing the biology and behavior of these pests can help individuals take proactive steps in prevention and treatment.


Types of Mites That Bite Humans
Understanding the different types of mites that bite humans is crucial for accurate identification and effective response to infestations. Mites can cause significant discomfort and health issues, and knowing the specifics about each type aids in both prevention and treatment. This section delves into the varieties of biting mites, including scabies, chiggers, and bird and rodent mites, providing important insights into their characteristics and behaviors.
Scabies Mites
Transmission and Life Cycle
Scabies mites, scientifically known as Sarcoptes scabiei, are highly contagious parasites. They spread primarily through skin-to-skin contact, making crowded living conditions a significant risk. Understanding their life cycle is vital since these mites can thrive in human environments. Female mites burrow into the skin, laying eggs that hatch into larvae. Within weeks, the new mites mature and continue the cycle, enhancing the risk of widespread transmission. The key characteristic of scabies mites is their ability to reproduce rapidly, which can lead to entire communities being affected within short periods. This aspect is essential for readers to appreciate the urgency of prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of Scabies Bites
The symptoms of scabies bites are typically intense itching, especially at night, and the formation of red, pimple-like irritations on the skin. These rashes often appear in clusters, and the affected areas may become inflamed and crusted if scratched. Recognizing the unique features of scabies symptoms is essential as they differ from other skin irritants. Notably, the intense itching is a distinguishing factor that can help in identifying this condition early. Overall, understanding these symptoms aids in recognizing scabies, contributing to timely medical intervention and the prevention of further spread.
Chigger Mites
Habitat and Behavior
Chigger mites, belonging to the Trombiculidae family, prefer to inhabit areas with dense vegetation and grasses. They are more prevalent in warm, humid environments where they can easily find hosts. These mites do not burrow into the skin but rather attach themselves and feed on skin cells, which can lead to considerable irritation. The important characteristic of chigger mites is their feeding behavior; they inject saliva that dissolves skin cells, creating the intensely itchy welts associated with their bites. This uniqueness is informative as it highlights how chigger bites can be mistaken for other insect bites.
Identification of Chigger Bites
Identifying chigger bites can be challenging since they often resemble other skin irritations. However, chigger bites usually present as a series of small, red welts, often clustered in areas where the skin is tight, such as around the ankles, waist, or under the arms. The key characteristic is the timing of the itching, which typically begins several hours after the bite. This delayed reaction is notable and helps distinguish chigger bites from other insect bites, thus informing readers about the correct recognition of these pests.
Bird and Rodent Mites
Common Species Overview
Bird and rodent mites are often associated with the nests of their hosts. The most common species include the Northern fowl mite and the tropical rat mite. These mites temporarily infest humans when their typical hosts are removed. Understanding these specific species allows one to comprehend the niche in which they operate. This knowledge is beneficial for educating readers about potential exposure and the need for vigilance in environments surrounding bird and rodent nests.
Signs of Infestation
Signs of infestation from bird and rodent mites include unexplained bites, itching, and finding the mites in bedding or clothing. These signs can be subtle, making it easy to overlook early infestations. The key characteristic of these mites is their tendency to be opportunistic; they will find human hosts when their original animal hosts are absent. Recognizing the signs of infestation early can provide critical insights into mitigating potential health risks.
Identifying Mite Bites on Human Skin
Identifying mite bites on human skin is a crucial aspect of understanding how to manage and treat these irritating nuisances. It serves as the first step in differentiating mite bites from other skin irritations, such as bug bites or allergic reactions. A correct identification contributes to effective treatment and can reduce unnecessary discomfort. Factors like visual characteristics, accompanying symptoms, and locations of the bites all play significant roles in aiding accurate identification. It's important for individuals to recognize these signs, as this knowledge empowers them to seek timely intervention and prevent further complications.
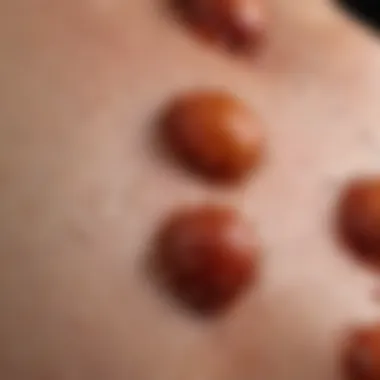
Visual Characteristics
Color and Texture
When examining the color and texture of mite bites, distinctive features emerge. Mite bites often present as small, red welts or bumps on the skin. The color can vary from pink to deep red depending on skin tone and response to the bite. A key characteristic is the raised nature of the lesions, combined with a smooth or slightly rough texture. This texture can hint at the severity of the bite and the individual's reaction.
This visual detail is beneficial for clarification in this article, as people may confuse mite bites with other insect bites. The raised surface often suggests irritation due to the mite's saliva, which is injected during feeding. This unique feature is significant; it aids discussions on management and treatment decisions related to mite infestations.
Common Locations on the Body
Common locations on the body where mite bites may occur are equally informative. These bites typically show up in areas where skin is thinner, such as between the fingers, on the wrists, or behind the knees. Recognizing these specific areas can help narrow down the potential source of irritation.
The importance of these common locations lies in their prevalence. This is a beneficial focus for this article because knowing where mite bites are likely to appear can assist individuals in conducting self-assessments more effectively. They can recognize patterns over time and possibly correlate environmental factors with the appearance of these bites.
Accompanying Symptoms
Itching and Inflammation
Itching and inflammation are significant symptoms often accompanying mite bites. The intensity of itching can vary based on the individual's sensitivity and the type of mite involved. This scratching response may lead to further inflammation, making the situation worse. A hallmark of mite bites is that they tend to cause considerable discomfort, which can disrupt daily activities.
Highlighting this symptom is valuable in this article, as it draws attention to how these sensations indicate an immune response to the mite's saliva. Understanding the itchiness allows for better comprehension of the need for effective treatment and can prompt readers to seek medical advice sooner.


Rash Development
Rash development is another vital aspect related to mite bites. Initially, a mild rash may manifest near the bite site, gradually expanding and becoming more pronounced with time. The rash may appear as small red spots or a more generalized area of redness, which can indicate an allergic reaction to the bite.
This characteristic is beneficial because it serves as a visible sign of the immune system's response to the allergens present in the mite's saliva. Knowing about this potential rash helps readers understand what to look for and encourages a proactive approach to dealing with mite infestations.
Understanding these visual characteristics and accompanying symptoms fosters a deeper recognition of mite bites, ultimately guiding individuals toward effective treatments and preventive measures.
Diagnosing Mite Bites
Diagnosing mite bites is essential for effective treatment and management. Mite bites can resemble various skin conditions, leading to potential misdiagnosis. Given this overlap, understanding the nuances in symptoms and presentation is critical. Accurate diagnosis not only helps alleviate immediate discomfort but also prevents complications that may arise from untreated bites or infestations. Furthermore, proper diagnosis can inform preventative strategies to reduce exposure to these pests.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Consultation with a healthcare professional should be a priority when mites bites are suspected. They offer expertise that distinguishes mite bites from similar skin issues, such as other insect bites or allergic reactions. Healthcare professionals can conduct a thorough assessment that includes reviewing medical history and symptoms.
During the consultation, patients are encouraged to provide detailed descriptions of their experience. This includes the onset, duration, and nature of the itching or rash. Such information can significantly impact the diagnostic process. The professional may also inquire about exposure to environments where mites are likely present, such as areas with poor hygiene or exposure to infested pets.
Overall, seeking professional advice sets the foundation for an accurate and timely diagnosis, ultimately leading to more effective treatment.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Skin Scraping and Microscopy
Skin scraping and microscopy are valuable diagnostic tools in identifying mite bites. This process involves taking a sample from the affected skin to observe under a microscope. The key characteristic of this method is its ability to reveal whether mites or their eggs are present, providing direct evidence of an infestation.
Skin scraping is a popular choice because it is minimally invasive and can yield immediate results. The unique feature of this procedure is its direct observation of the causative agents. If mites are detected, it allows the healthcare provider to confirm the diagnosis and tailor the treatment plan specifically to the type of mite involved. However, one disadvantage is the need for skilled hands, as improper technique can lead to inaccurate results.
Clinical Criteria for Diagnosis
Clinical criteria for diagnosis involve a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms and presentation characteristics. This method relies on established guidelines that differentiate mite bites from other conditions. The primary aspect of this diagnosis is the recognition of specific symptoms associated with different mite species.
Using clinical criteria is beneficial because it leverages existing medical knowledge to expedite diagnosis. This approach is effective in many cases where skin scraping may not be immediately available. Its unique feature is the reliance on observable symptoms and patient history, which can be advantageous for rapid assessment. However, the reliance on clinical criteria alone may sometimes lead to misdiagnosis, particularly in atypical presentations of symptoms. Thus, it is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic methods for the best outcomes.
Treatment Options for Mite Bites
Understanding treatment options for mite bites is crucial. Timely intervention can alleviate discomfort and prevent more serious infections or complications. Mite bites might lead to various reactions, such as irritation and itching. Choosing the right treatment helps in managing symptoms effectively.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments offer direct relief to areas affected by mite bites. These options work on the skin surface, providing immediate comfort to irritated skin.
Anti-itch Creams
Anti-itch creams contain ingredients like hydrocortisone or calamine. These agents soothe inflammation and reduce itching. Their immediate action makes them a favorite among those suffering from skin reactions. Anti-itch creams are convenient and easy to apply. However, it is essential to use them as directed to avoid skin thinning or irritation.
Medicinal Ointments
Medicinal ointments offer more potent relief for severe reactions. Often containing active ingredients like corticosteroids or other anti-inflammatory agents, they can address underlying issues causing discomfort. The key characteristic of medicinal ointments is their ability to penetrate skin layers, providing deeper relief. While beneficial for significant symptoms, improper use can lead to side effects like skin atrophy or increased risk of infections.
Oral Medications
Oral medications provide systemic relief for itchiness and allergy-like symptoms. These treatments may be preferred for more extensive outbreaks or persistent itching.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are effective in blocking histamine, a chemical responsible for allergic responses. This class of medications is popular due to its dual ability to alleviate itching and induce drowsiness. Many people choose over-the-counter antihistamines for quick relief. However, it is vital to be aware of potential side effects, such as sedation, which may limit daily activities.
Prescription Medications


Prescription medications include stronger antihistamines or corticosteroids. These are significant for more serious cases where over-the-counter options fall short. The unique feature of prescription medications is their tailored approach; a healthcare provider can adjust the dose based on individual needs. These can be highly beneficial, but they do carry risks, including possible dependency or adverse effects.
Always consult a healthcare provider for the best treatment options, particularly when symptoms persist or worsen.
Preventative Measures Against Mite Bites
Preventative measures against mite bites play a crucial role in minimizing the risk and impact of these infestations. Understanding environmental factors and implementing personal protection strategies are essential for reducing encounters with mites. This section explores actionable steps that can be taken to prevent mite bites, focusing on specific elements such as cleaning, disinfection, and protective clothing.
Environmental Management
Cleaning and Disinfection
Cleaning and disinfection are fundamental practices in managing mite-related issues. Keeping living spaces clean significantly contributes to reducing mite populations. Regular vacuuming, particularly in areas where mites thrive, like carpets, upholstery, and bedding, is essential.
The key characteristic of this practice is its ability to remove not only dirt and debris but also the mites themselves. This method is particularly beneficial because it also addresses other allergens that can affect health.
One unique feature of cleaning practices is the use of hot water for laundering bedding and clothing, which can effectively kill mites. The advantages include a fresher environment and reduced risk of infestation, though the disadvantages might be the need for consistent effort and use of energy for hot washing.
Reducing Rodent and Bird Populations
Reducing rodent and bird populations is another effective measure to prevent mite bites. Rodents and birds can act as hosts for certain mites, such as bird mites and rodent mites. By eliminating food sources and nesting areas, one can effectively decrease potential mite colonies in the home vicinity.
The key characteristic of this approach lies in its preventative nature. It is a popular choice because it not only targets mites but also addresses broader pest issues in the environment.
The unique feature of this method is that it involves a combination of humane traps and exclusion techniques, which can be effective without harming wildlife. The advantages include a long-term reduction in pest populations; however, the disadvantages may include the challenge of ensuring comprehensive reduction across an area, which can sometimes require persistent attention and community involvement.
Personal Protection Strategies
Proper Clothing Choices
Making appropriate clothing choices can significantly decrease the likelihood of mite bites. Wearing tight-fitting clothing that covers as much skin as possible creates a barrier against mite contact. Selecting fabrics that are less permeable prevents mites from accessing skin.
The key characteristic of choosing the right clothing is its ability to serve as a physical deterrent. This strategy is beneficial because it provides immediate protection during outdoor activities.
One unique aspect of this approach is opting for light-colored clothing. Light colors may help with visibility, allowing for easier detection of ticks or mites that may have landed on the fabric. The advantages include enhanced protection and peace of mind during outdoor activities, whilst one potential disadvantage is discomfort in warm weather.
Use of Repellents
Utilizing repellents is another effective strategy to prevent mite bites. Insect repellents containing DEET or picaridin can create a barrier that deters mites from landing on the skin. Choosing the right repellent can significantly enhance outdoor comfort.
The key characteristic of repellents is their active ingredient that disrupts the sensory mechanisms of the pests, making them less likely to approach. This measure is a popular choice among individuals who spend time in areas prone to mite infestations.
A unique feature of repellents is their varied formulations, including sprays, sticks, and lotions, which offer flexibility in application. The advantages include ease of use and effectiveness, while a disadvantage might be the need for reapplication, especially in humid or sweaty conditions.
Overall, the integration of environmental management and personal protection strategies plays a central role in preventing mite bites, educating individuals on effective measures and fostering awareness about these often-overlooked pests.
Finale
The conclusion serves as a crucial part of the article, encapsulating the essential elements discussed throughout the text. Understanding mite bites goes beyond mere identification; it involves recognizing their implications on human skin and overall health. Mite bites, while commonly overlooked, can lead to significant discomfort and, in some cases, severe health complications. This makes it vital for individuals, especially educators, healthcare professionals, and veterinarians, to have a comprehensive understanding of these pests.
Recapitulating Key Points
In this article, several key points were covered:
- Types of Mites: We explored the different species of mites that bite humans, including scabies, chiggers, and bird or rodent mites. Each type has unique characteristics and symptoms that are essential for accurate identification.
- Identifying Characteristics: Recognizing the visual aspects of mite bites is crucial. Color, texture, and common locations on the body were discussed, providing readers with the tools to differentiate mite bites from other skin irritations.
- Diagnostic Approaches: The process of diagnosing mite bites often requires professional insight. The article detailed the importance of consulting healthcare providers and understanding various diagnostic tests like skin scraping.
- Treatment Options: Effective management of mite bites includes topical treatments and oral medications. Readers are advised about different remedies and when to seek professional help.
- Preventative Measures: Strategies for mitigating the risk of mite bites were highlighted, including environmental management and personal protective actions.
These points underline the significance of informed decision-making when it comes to recognizing and managing mite bites.
Future Implications for Mite Management
Looking ahead, the implications for mite management are broad and important. As urbanization increases and environmental changes continue, the interaction between humans and mites may evolve. Future research should focus on these areas:
- Research on Resistance: As with other pests, mites can develop resistance to treatments. Investigating this phenomenon will be crucial for developing new, effective management strategies.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Increasing understanding of mite-related issues is vital. Targeted campaigns can educate the public, enabling more people to recognize symptoms and seek timely help.
- Collaboration Between Fields: Various disciplines such as health care, veterinary services, and environmental science must work together. This collaboration can lead to innovative solutions and better prevention strategies.
In summary, managing mite bites effectively requires ongoing education, awareness of evolving challenges, and collective approaches to tackling these persistent pests.















