Understanding Phoenix Cockroaches: Unique Traits and Roles


Intro
Phoenix cockroaches are a fascinating yet frequently ignored species within the larger context of insect biodiversity. This article aims to uncover the various facets that define these remarkable creatures. By highlighting their unique characteristics, habitats, lifecycle, feeding habits, and ecological roles, we can gain a deeper appreciation for them. Additionally, we will address misconceptions that surround cockroaches as a whole and consider their potential as pets.
Animal Profile
General Overview
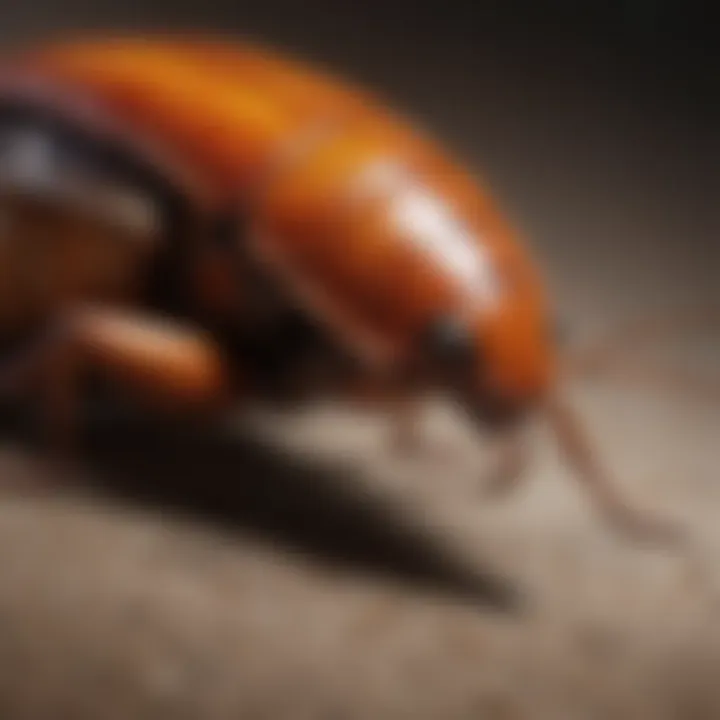
Phoenix cockroaches (Gromphadorhina portentosa) belong to the family Blaberidae. They are known for their sizeable stature, often reaching lengths of 4 to 5 inches. Their bodies are robust, covered in a hard exoskeleton that can range from light brown to almost black in color. Unlike the common house cockroach, these insects are mostly non-flying and instead rely on their strong legs for movement, making them well-suited for terrestrial habitats.
Habitat and Distribution
These cockroaches are native to Madagascar, where they thrive in tropical climates. They prefer warm, humid environments typically found in dense foliage and leaf litter. In captivity, it is crucial to replicate these conditions to ensure their well-being. Thus, pet owners should maintain humidity levels between 40-60% and temperatures around 75-85°F.
Fascinating Facts
Unique Traits and Adaptations
Phoenix cockroaches exhibit some unique adaptations that set them apart from other species. They possess strong mandibles, which enable them to chew tough plant materials, including decaying wood and leaves. Their impressive size can deter potential predators, while their behavior of playing dead when threatened is an effective survival strategy.
Historical and Cultural Significance
In some cultures, cockroaches, including the Phoenix variety, are seen as symbols of resilience due to their ability to survive under harsh conditions. In art and folklore, they often appear as representations of survival and adaptability.
Conservation Status
Current Population Trends
Currently, Phoenix cockroaches are not classified as endangered. However, their habitats are subject to threats due to deforestation and habitat loss in Madagascar. Monitoring their population trends is essential to ensure that they do not face significant decline in their natural environment.
Threats and Challenges
Habitat destruction remains one of the foremost threats to their population. Additionally, the pet trade can sometimes pose risks, as sustainability practices are not always followed. Increasing awareness of responsible sourcing and conservation is vital to preserving their natural habitats.
Care Tips for Pet Owners
Basic Needs and Requirements
When keeping Phoenix cockroaches as pets, it's vital to provide an environment that mimics their natural habitat. Proper housing is essential:
- A terrarium with good ventilation and adequate space.
- Substrate that retains moisture, such as coconut fiber or peat moss.
- Hiding spots using cardboard, wood, or other materials.
Health and Wellness Tips
Regular monitoring of temperature and humidity levels is crucial for their health. A nutritious diet consisting of fruits, vegetables, and commercial insect feed ensures they receive adequate nutrition. Removing uneaten food promptly helps to maintain cleanliness and prevent mold growth.
Prolusion to Phoenix Cockroaches
Phoenix cockroaches, often overlooked in discussions about entomology, deserve attention due to their unique features and ecological significance. Understanding these insects is crucial for combatting misconceptions and highlighting their role in various environments. Their unique behaviors and characteristics provide insights into resilience and adaptability in the face of modern environmental challenges. The exploration of Phoenix cockroaches not just enriches our comprehension of biodiversity but also fosters appreciation for lesser-known species.
General Overview and Characteristics
Phoenix cockroaches, scientifically known as Gromphadorhina portentosa, are notable members of the cockroach family. They exhibit various striking characteristics. Typically robust and large, these insects can grow up to 4 inches in length. Their exoskeleton varies in color from a dark brown to a reddish hue, offering them subtle camouflage among their natural habitat.
Their physical structure includes long antennae that provide sensory functions, enhancing their ability to navigate and respond to environmental stimuli. This sensory adaptation is critical, as it aids in foraging and social behavior. Phoenix cockroaches are nocturnal, preferring to be active at night, which is common among many cockroach species. Their diet consists mainly of decaying organic matter, making them vital decomposers in their ecosystems.
In terms of behavior, Phoenix cockroaches show both solitary and social tendencies. They engage in various forms of communication, using pheromones and tactile signals. This enables them to maintain social bonds and coordinate activities in their groups.


Species Classification and Taxonomy
The classification of Phoenix cockroaches falls under the order Blattodea and the family Blaberidae. Within this taxonomy, they represent a specific genus that is distinct for various reasons. Understanding the taxonomical hierarchy is important, as it not only reflects the evolutionary lineage but also aids in studying the relationship between different species.
The Blaberidae family encompasses other well-known cockroach species, yet Phoenix cockroaches have distinctive traits that set them apart. These insects are often studied in entomological research due to their unique breeding habits and adaptive characteristics. Their classification highlights their ecological niche and the importance of their role in the ecosystem.
Phoenix cockroaches are not merely pests; they are essential contributors to nutrient cycling and ecosystem health.
Understanding the taxonomy of Phoenix cockroaches allows for better insights into their biology and behavior. It forms a foundation for further research and contributes to ecological studies aimed at preserving biodiversity.
Habitat and Distribution
The habitat and distribution of Phoenix cockroaches are fundamental to understanding their biology and behavior. These factors greatly influence their survival, reproduction, and interactions with other species. A thorough examination of their native environments has practical applications when it comes to care and habitat setup for those who choose to keep them as pets. Knowing where they thrive can also aid in dispelling myths surrounding their existence and habitat needs.
Natural Habitat of Phoenix Cockroaches
Phoenix cockroaches primarily inhabit warm, dry climates, often found in desert regions. Their native environments include areas with a mix of rocks, sand, and sparse vegetation, which provide shelter and organic material for their diet. This is crucial as it allows the cockroaches to escape the heat and hide from predators. They tend to thrive in places where moisture is relatively low, such as under rocks or in crevices, which contribute to their unique adaptations for survival.
In captivity, replicating their natural habitat becomes essential for their well-being. A suitable enclosure must mimic these elements, with a substrate that allows them to burrow and hide. The balance of humidity is also a key consideration, as excess moisture can lead to health problems. Creating a habitat that reflects their natural conditions helps maintain their health and supports their natural behaviors.
Geographical Distribution
Phoenix cockroaches are predominantly found in the southwestern United States, particularly in Arizona, which is their main habitat. They are also found in parts of Mexico. The distribution of these cockroaches is primarily limited to regions that offer their preferred environmental conditions.
Their geographical range highlights the importance of protecting these habitats from human encroachment and climate change. As urban development expands, the areas where Phoenix cockroaches thrive are increasingly threatened, making it essential to educate the public about their ecological significance.
In summary, recognizing the natural habitat and geographical distribution of Phoenix cockroaches enriches our understanding of their needs and the measures necessary for conservation. This knowledge not only helps in the care of these unique creatures as pets but also emphasizes the need for awareness and protection of their natural environments.
Life Cycle of Phoenix Cockroaches
Understanding the life cycle of Phoenix cockroaches is essential for various reasons. This knowledge informs us about their reproduction, development, and lifespan, which are crucial for anyone studying entomology or considering these insects as pets. Their life cycle stages, from egg to adult, shed light on their survival mechanisms in natural habitats. This understanding enables researchers and enthusiasts to appreciate the complexity of their biology and ecology.
Egg Stage and Development
Phoenix cockroaches start their life cycle as eggs. Female Phoenix cockroaches lay egg cases known as oothecae. Each ootheca contains several eggs, and the number can range from 30 to 50. The egg cases are often hidden in the substrate of their habitat, providing protection from predators.
The development of Phoenix cockroach eggs typically takes about 60 days, depending on environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity. Warmer temperatures can accelerate development, while cooler temperatures may slow it down. After maturation, the eggs hatch into nymphs, marking the beginning of the next stage of their life cycle.
Nymph Stage Characteristics
Nymphs are the immature stages of Phoenix cockroaches. They differ from adults in several ways. For instance, nymphs are smaller, lack fully developed wings, and have a softer body. As nymphs grow, they undergo several molts, shedding their exoskeletons to accommodate their growing bodies. This molting process is crucial for their development and can occur roughly 6 to 8 times over several months.
During this period, nymphs are highly active and often forage for food, which is essential for their growth. Their diet consists mainly of plant matter, which provides the necessary nutrients for their immature bodies. Understanding the nymph stage is important for individuals who want to care for them as pets, as proper nutrition is vital for healthy growth.
Adult Emergence and Lifespan
Once they complete their nymph stages, Phoenix cockroaches reach adulthood. Adult cockroaches display full physical characteristics, including developed wings and reproductive organs. Adult males tend to be larger than females and can be distinguished easily.
The adult lifespan of Phoenix cockroaches averages around 2 to 3 years in captivity, though this may vary depending on living conditions, diet, and overall care. Once they reach adulthood, they are capable of reproduction, effectively continuing the cycle. Notably, adults can also adapt to various habitats, which speaks to their resilience as a species. Their longevity and reproductive capabilities make them fascinating subjects for study and a compelling choice for those interested in keeping insects as pets.
The life cycle of Phoenix cockroaches intricately showcases their ability to thrive in diverse environments, making them an interesting species in the world of cockroaches.
Feeding Habits
Feeding habits are vital to understanding the overall health and behavior of Phoenix cockroaches. Their dietary preferences not only reflect their ecological niche but also influence their interactions with the environment. This section will delve into their diet, nutritional needs, and feeding behaviors in the wild, providing a comprehensive view of how these factors contribute to their role within their habitat.
Diet and Nutritional Needs
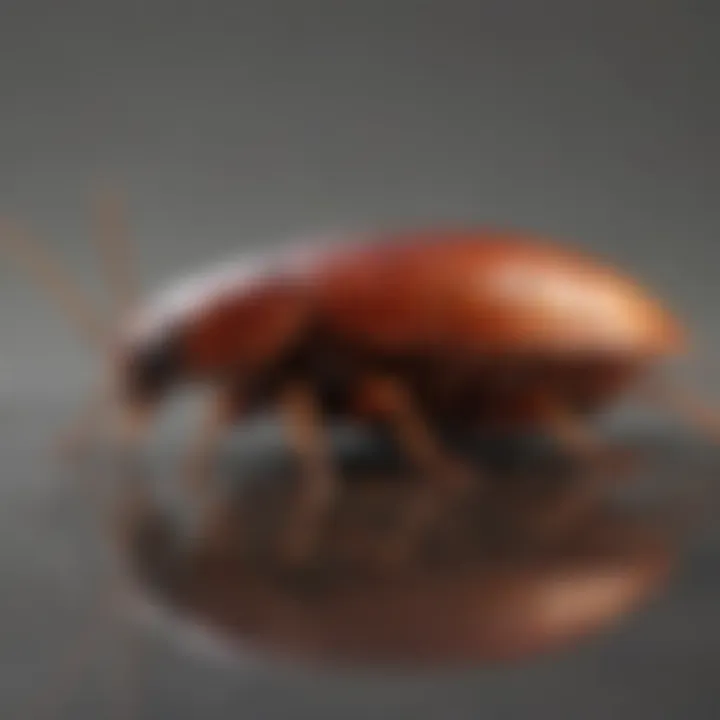


Phoenix cockroaches are primarily herbivorous. Their diet consists mainly of decomposing plant matter, leaf litter, and fruits. Understanding their nutritional needs is crucial for both their survival in the wild and their care in captivity.
- Fruits and Vegetables: These cockroaches consume a variety of fruits and veggies. Carrots, apples, and bananas are common favorites.
- Fungi: Decaying fungi forms an important part of their diet, providing various nutrients.
- Leaf litter: Ground cover rich in organic material offers essential fiber and minerals.
A balanced diet helps Phoenix cockroaches maintain optimal health. Nutritional imbalance can lead to poor growth and lower resistance to diseases. In captivity, it's important for pet owners to replicate this diet properly, ensuring the cockroaches receive adequate vitamins and minerals.
Feeding Behavior in the Wild
In their natural habitat, Phoenix cockroaches exhibit interesting feeding behaviors. They are typically nocturnal, which affects their foraging patterns.
- Foraging Strategy: These cockroaches use their antennae and sensory receptors to locate food efficiently in dark environments.
- Group Feeding: They often feed in small groups, allowing them to utilize resources more effectively while reducing the risk of predation.
- Food Selection: Their ability to process and utilize decaying organic matter allows them to contribute significantly to decomposition and nutrient cycling in their ecosystem.
As decomposers, their feeding habits play a crucial role in breaking down organic materials. This, in turn, enriches the soil and supports plant growth. Overall, the feeding habits of Phoenix cockroaches not only reflect their ecological adaptations but also highlight their importance in the broader context of environmental health.
Behavioral Aspects
Understanding the behavioral aspects of Phoenix cockroaches is crucial for several reasons. First, their social interactions and communication can provide insights about their survival strategies in the wild. Second, their adaptations to environmental changes reveal how resilient and resourceful these insects can be. In studying these behaviors, we gain a deeper appreciation of their ecological role, which extends beyond mere existence.
Social interactions and Communication
Phoenix cockroaches exhibit a variety of social behaviors that are essential for their survival. These insects are primarily social creatures. They often communicate through chemical signals known as pheromones. This form of communication plays a key role in coordinating their activities, like foraging or mating. They are known to live in colonies, which offers protection against predators and enhances their chances for reproduction.
During interaction, they also engage in subtle physical gestures. These may include antennae twitches and body postures that signal comfort or alarm. The ability to communicate effectively allows them to establish social hierarchies. Typically, dominant individuals control resources within the group, which helps maintain order.
- Chemical Communication: The use of pheromones for signaling.
- Physical Gestures: Antennae movement and posture signaling.
- Social Hierarchies: Dominance dynamics within colonies.
Social interactions are a cornerstone of Phoenix cockroach behavior, leading to improved survival rates and reproductive success.
Adaptations to Environment
Phoenix cockroaches showcase fascinating adaptations that allow them to thrive in varying environments. These adaptations are not only physical but also behavioral. For instance, they possess tough exoskeletons that protect them against environmental stresses, such as desiccation in dry climates. This aspect of their biology is particularly significant, as it demonstrates their capacity to live in diverse habitats.
Their behavioral adaptations are equally remarkable. Phoenix cockroaches can alter their activity patterns based on environmental conditions. For example, during periods of excessive heat, they may become less active, conserving energy and moisture. Conversely, they tend to be more active during cooler parts of the day or night, which aids in their survival by allowing them to forage without excessive risk.
- Tough Exoskeleton: Protects against environmental threats.
- Activity Pattern Adjustments: Changes based on temperature and humidity levels.
Understanding these adaptations not only informs us about the resilience of Phoenix cockroaches but also highlights their significance in ecological research and conservation efforts.
Role in the Ecosystem
Phoenix cockroaches play an essential role in their ecosystem, contributing significantly to environmental health and stability. As decomposers, they facilitate the breakdown of organic matter, enriching the soil and supporting plant growth. Their feeding habits and interactions with other species create a balanced ecosystem that nurtures biodiversity.
Decomposers and Nutrient Cycling
One of the most vital functions of Phoenix cockroaches in the ecosystem is their role as decomposers. They thrive on decaying organic materials such as leaves, wood, and other plant debris. This feeding behavior not only aids in waste reduction but also promotes nutrient cycling. As they consume waste, they break it down into simpler compounds. Consequently, the nutrients released in the process become available to plants. This cycle is crucial as it sustains the health of ecosystems and supports various life forms.
Benefits of Nutrient Cycling:
- Soil Enrichment: The waste excreted by Phoenix cockroaches contains essential nutrients that improve soil quality.
- Enhanced Plant Growth: By decomposing organic materials, they promote healthier ecosystems conducive to plant life.
- Biodiversity Support: Healthy, nutrient-rich soils can support a wider variety of plant species, which in turn supports more animal species.
In this manner, Phoenix cockroaches serve as a bridge between organic waste and plant health, making them indispensable to their habitats.
Interactions with Other Species
Phoenix cockroaches engage in various interactions with other species within their ecosystems. These relationships can be mutualistic, commensal, or predatory, each contributing to the overall balance of the environment.
Types of Interactions:

- Mutualism: Some fungi and bacteria thrive in environments that include Phoenix cockroaches, benefiting from the nutrients in their feces, while the cockroaches help distribute these microorganisms across the soil.
- Predation: They serve as prey for various animals such as birds, reptiles, and small mammals. This predation keeps cockroach populations in check and supports the food chain.
- Symbiotic Relationships: Other invertebrates may inhabit areas influenced by cockroaches, benefiting from the decomposed material and engaging in complex interactions.
Interactions with other species emphasize the importance of Phoenix cockroaches in maintaining ecological balance. They are vital components of food webs, ensuring that ecosystems remain healthy and functioning.
In summary, Phoenix cockroaches are significant players in their ecosystems. They support nutrient cycling through decomposition and engage in vital interactions with other species, reinforcing the interconnectedness of life within their habitats.
Common Misconceptions
Understanding common misconceptions about Phoenix cockroaches is vital for fostering a better narrative surrounding these insects. They are often mistakenly perceived as threats to human health or as unsightly pests. Such views can overshadow the ecological importance of these creatures and ultimately hinder appreciation for their role in the environment. By clarifying myths and presenting facts, we can pave the way for a more informed opinion about Phoenix cockroaches.
Cockroaches as Pests
Many people categorize Phoenix cockroaches strictly as pests without recognizing their unique traits. It is important to define what makes a pest. Generally, pests are organisms that cause harm or discomfort to humans and their environments. While it is true that some cockroach species can be vectors for diseases and may infest homes, Phoenix cockroaches do not share these characteristics. They are larger and more robust compared to typical household cockroaches. In fact, they rarely venture into human living spaces.
Furthermore, Phoenix cockroaches have become popular in the exotic pet trade due to their docile nature and fascinating behaviors. Many enthusiasts appreciate them for their beauty and ornate exoskeletons, finding them captivating rather than troublesome. Thus, it is essential to differentiate between harmful species and harmless ones like the Phoenix cockroach.
Key Points
- Phoenix cockroaches are not typical pests.
- Their size and behavior reduce the likelihood of them infesting human environments.
- They are appreciated in the exotic pet community.
Cockroaches and Disease Transfer
The perception that all cockroaches are carriers of disease can lead to unwarranted fear. While several species, such as the German cockroach, are known to be associated with various health risks, this does not apply to Phoenix cockroaches. They are not known to transmit diseases to humans and do not pose significant health risks.
Research indicates that Phoenix cockroaches primarily inhabit tropical environments and are not found in urban settings, where they could potentially interact with humans. Thus, their role in disease transfer is minimal. Many studies indicate that it is unnecessary to lump this species in with other cockroaches that have negative connotations in public discourse.
Important Considerations
- Phoenix cockroaches do not carry diseases harmful to humans.
- They have different living conditions compared to more harmful species.
- Education can aid in changing perceptions about these insects.
Understanding these misconceptions helps reduce unnecessary fear and promotes a more balanced view towards Phoenix cockroaches. By educating ourselves, we not only demystify these creatures but also appreciate their essential roles in ecosystems.
Phoenix Cockroaches as Pets
Phoenix cockroaches are gaining attention in the realm of exotic pets. Their unique characteristics, sizes, and relatively low maintenance needs make them appealing to various enthusiasts. Within this section, we will explore the essential elements that make Phoenix cockroaches suitable as pets. We will discuss care requirements and habitat setup, followed by the benefits associated with owning them.
Care Requirements and Habitat Setup
Ensuring the well-being of Phoenix cockroaches requires an understanding of their needs. The essentials include:
- Enclosure: A well-ventilated glass or plastic terrarium works best. The size should be at least 20 gallons for a small colony.
- Substrate: Use coconut fiber or mixed substrate as a base. This allows for burrowing, which is a natural behavior.
- Temperature and Humidity: Maintain a temperature range of 75°F to 85°F, with humidity levels between 40% and 60%. Providing a heat mat can help achieve optimal conditions.
- Decor: Include hiding spots such as cardboard tubes or leaf litter to create a stimulating environment. Adding branches can also provide climbing opportunities.
- Diet: A balanced diet is crucial. Feed them fresh vegetables, fruits, and specialized roach food to ensure proper nutrition. Avoid citrus fruits as they may harm cockroaches.
Regular monitoring of the habitat conditions is vital. Adjustments might be necessary based on observed behaviors or any signs of stress.
Benefits of Keeping Cockroaches as Pets
Keeping Phoenix cockroaches as pets can offer unique advantages. Some notable benefits include:
- Educational Value: Owning these insects can serve as a fascinating educational tool. They provide insights into entomology and ecosystem dynamics, beneficial for students and educators.
- Low Maintenance: Compared to traditional pets, Phoenix cockroaches are less demanding. They do not require daily walks or grooming.
- Sustainable Pet Choice: They contribute to sustainability efforts. Keeping them as pets can reduce the demand for other exotic pets that may harm populations in the wild.
- Captivating Behavior: Observers often find their behaviors intriguing. The way they interact with their environment and each other can be a source of endless fascination.
"Phoenix cockroaches showcase that not all pets need to conform to traditional standards to be valuable companions."
Finale and Future Research Directions
Summary of Findings
This article has explored several aspects of Phoenix cockroaches, including their characteristics, life cycle, feeding habits, and ecological role. Phoenix cockroaches, often misunderstood, play significant roles within their ecosystems. They contribute to nutrient cycling and aid in decomposition processes. Their dietary preferences highlight their adaptability, consuming organic matter and helping maintain ecological balance. Significant details such as their unique communication methods and social structures also emerged. This comprehensive analysis reveals that the Phoenix cockroach's behavior aligns with broader patterns observed across many insect species, providing an interesting case for further study.
Implications for Conservation and Awareness
Recognizing the importance of Phoenix cockroaches extends beyond scientific curiosity. Their ecological role as decomposers accentuates their significance in maintaining healthy environments. Promoting awareness of these insects could lead to better conservation strategies, particularly in habitat-preserving efforts. Misconceptions surrounding cockroaches often lead to their unjust extermination. A shift in perception can foster an appreciation for the natural world and encourage responsible stewardship. Future research should focus on conservation practices that embrace the benefits of all species, including those less considered, like the Phoenix cockroach.
When we acknowledge the contribution of every species, we pave the way for a more balanced ecosystem.
Increasing public understanding can ultimately nurture a deeper respect for biodiversity, recognizing that even the smallest species holds importance in the intricate web of life.















