Understanding Ticks in the Ear: Symptoms and Treatments
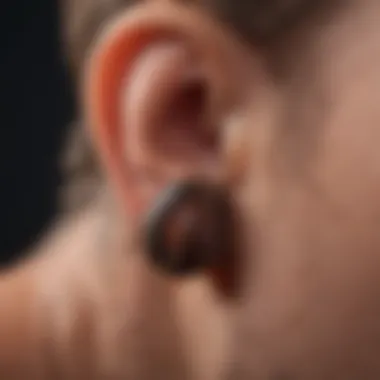

Intro
Ticks are often portrayed as minor nuisances, but their presence in the ear can indicate a much larger issue. These blood-sucking parasites can cause serious discomfort and health problems for both humans and pets. The importance of understanding ticks in the ear cannot be overstated. This comprehensive guide will delve into various aspects of ticks, including their biology, symptoms associated with infestations, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Animal Profile
General Overview
Ticks belong to the class of arachnids, which makes them relatives of spiders and scorpions. They are ectoparasites, feeding on the blood of mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians. Notably, there are more than 900 species of ticks worldwide, with some being more prevalent in specific regions. Among the ticks, the Ixodes species are particularly concerning due to their role in transmitting diseases such as Lyme disease.
Habitat and Distribution
Ticks thrive in various habitats, largely depending on the climate and the availability of hosts. They can be found in wooded areas, grasslands, and gardens. High humidity and moderate temperatures support their lifecycle. During warmer months, ticks tend to be more active and often seek out hosts, making it essential to be vigilant during outdoor activities. Their ability to conceal themselves in fur, hair, or behind the ears increases the risk of infestation, especially in pets and children.
Fascinating Facts
Unique Traits and Adaptations
Ticks possess unique adaptations that enable them to survive in diverse environments. They have specialized mouthparts, allowing them to attach firmly to their host and extract blood. Some species can survive for long periods without feeding, which allows them to wait for suitable hosts. Interestingly, ticks have developed the ability to sense carbon dioxide, helping them locate potential hosts from a distance.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Ticks have appeared throughout history, often associated with illnesses. Ancient cultures recognized their role in transmitting diseases. The various myths and stigma surrounding ticks often overshadow their ecological role. Despite their significance in the ecosystem, awareness about their health implications remains low.
Conservation Status
Current Population Trends
While many tick species are abundant, specific ones are under threat due to habitat loss and climate change. As populations fluctuate, the risk of zoonotic diseases can change as well. Significant focus on tick ecology is needed to understand how these shifts will impact human and animal health.
Threats and Challenges
Ticks face diverse threats, including habitat destruction and pesticides. Ironically, changes in climate can lead to ticks expanding their range, posing new risks to both wildlife and human populations. Understanding these challenges is vital for developing effective control strategies.
Care Tips for Pet Owners
Basic Needs and Requirements
Pet owners must ensure their pets are regularly checked for ticks, especially after outdoor activities. The use of preventive measures is essential. Products such as Frontline and NexGard can offer protection against ticks. Educating pet owners on the signs of tick infestations will also play a crucial role in health maintenance.
Health and Wellness Tips
Regular veterinary visits can help in the early detection of ticks. If ticks are found, it is imperative to remove them safely to prevent disease transmission. Home prevention measures are equally essential. Keeping lawns trimmed and using tick-repellent products can significantly reduce the risk of infestation.
Quote: Awareness and education are paramount in combating tick infestations, particularly in sensitive regions.
Understanding ticks in the ear involves recognizing their biology, the threats they pose, and adopting effective management practices. This guide aims to elevate awareness and provide actionable insights for mitigating risks related to these often-overlooked parasites.
Prolusion to Ticks
Ticks are small arachnids that pose significant health threats to both humans and animals. Understanding ticks is essential for recognizing how they interact with their environment and the potential dangers they bring. This section outlines the biological characteristics of ticks, their classifications, and the complexities of their life cycles.
What are Ticks?
Ticks are ectoparasites, which means they live on the outside of their hosts. They feed on blood from a variety of animals, including humans. These creatures belong to two primary families: Ixodidae (hard ticks) and Argasidae (soft ticks). Each kind has unique features and behaviors that can impact the assessment and management of tick-related issues.
Types of Ticks
Hard Ticks
Hard ticks are named for their tough outer shell, which provides a level of protection against environmental factors. This type is often more visible due to its size, which ranges from a few millimeters to larger ones that are nearly a centimeter long after feeding. They are known for their ability to latch onto hosts for several days while feeding. Their feeding behavior can lead to significant health risks, such as Lyme disease, making them a focal point for tick-related studies.
Soft Ticks
Soft ticks differ from their hard counterparts primarily in body structure. They have a leathery, flexible skin that allows for a different form of feeding. Their feeding periods are shorter, often lasting only a few minutes. Often smaller than hard ticks, soft ticks can still transmit diseases, although they are less commonly known to be involved in major disease outbreaks. Their unique feeding habits merit close observation within the spectrum of tick studies.

Life Cycle of a Tick
Ticks undergo a complex life cycle, which comprises four stages: egg, larval, nymph, and adult. This developmental process plays a crucial role in their survival, ability to infect hosts, and the management of their populations. Understanding the life cycle stages can aid in effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Egg Stage
The egg stage is a critical point in the tick life cycle. Female ticks lay thousands of eggs on or near their host environment. These eggs can survive adverse conditions, allowing them to hatch when the environment is favorable. This resilience is significant for population management since controlling adult ticks may not affect upcoming generations.
Larval Stage
In this stage, the tick emerges from its egg and is notably smaller than later life stages. Larvae require a blood meal to develop into the next stage, the nymph. This early feeding phase is crucial as it increases the potential for disease transmission, depending on the host they attach to. Understanding their feeding behavior at this stage can highlight possible health risks.
Nymph Stage
Nymphs are often responsible for transmitting diseases to humans, as they are small and can easily go unnoticed. This stage follows the larval phase and also requires a blood meal. Their size makes detection difficult, increasing the likelihood of a bite going unrecognized until symptoms develop. Proper recognition of this stage enhances awareness and preventive measures.
Adult Stage
In the adult stage, ticks are fully developed and capable of reproducing. They are larger and easier to spot compared to nymphs and larvae. This stage is critical not only for procreation but also for the spread of diseases like Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Understanding their behavior and habitat preferences can significantly aid in tick management efforts.
Understanding the life cycle of ticks is essential for preventing tick-borne diseases and effectively managing infestations.
Ticks in the Ear
Ticks in the ear represent a significant yet often overlooked health concern for both humans and pets. Recognizing the implications of tick infestations in this sensitive area is crucial. This section aims to unravel the complexities associated with ear ticks, explaining their typical behaviors, potential risks, and the necessity for awareness and prevention strategies.
Understanding Tick Infestation
In order to grasp the seriousness of ticks in the ear, it is essential to understand tick infestation thoroughly. Ticks usually thrive in outdoor environments, particularly in grassy or wooded areas. They tend to latch onto skin directly when in proximity to hosts, including humans and pets. Once attached, ticks begin to feed on blood, and in doing so, they can transmit various diseases. Infestations can be symptomatic or asymptomatic, but often lead to noticeable discomfort.
Ticks transmit pathogens while feeding, making them vectors for diseases. This underscores the importance of prompt identification and management of tick infestations. When ticks invade the ear, they may cause inflammation, infection, and other complications if left untreated. Awareness of how infestations occur can aid individuals in taking preventative measures to protect themselves and their pets from these parasites.
Common Types of Ticks Found in Ears
Dermacentor Variabilis
Dermacentor Variabilis, commonly known as the American dog tick, holds notable significance when discussing ticks in the ear. This tick is recognized for its ability to transmit diseases such as Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia. One of the key characteristics of Dermacentor Variabilis is its pronounced size and distinctive markings, making it somewhat easier to identify compared to other tick species.
The unique feature of Dermacentor Variabilis is its preference for dogs as hosts, although it can also latch onto humans. This tendency emphasizes the tick's impact on household pets and the indirect risks it poses to human health. Awareness of its existence can help tackle infestations more effectively, allowing for early identification and action. However, a disadvantage lies in its prevalence, which means encountering it when outdoors is quite likely.
Rhipicephalus Sanguineus
Rhipicephalus Sanguineus, also known as the brown dog tick, is another significant species found in the ear. This tick is commonly associated with dogs but can also affect humans, particularly in environments where pets are kept. A noteworthy characteristic of Rhipicephalus Sanguineus is its habitat preference; it often inhabits warmer indoor areas, such as dog kennels.
This tick's ability to breed indoors poses a unique challenge, as simply treating outdoor environments might not eliminate the problem. A unique feature of Rhipicephalus Sanguineus is its capacity to thrive in close quarters with canine companions, raising the likelihood of tick transmission between them and pet owners. Its presence can lead to severe complications such as canine ehrlichiosis, thus requiring vigilant monitoring and preventive measures among pet owners.
Awareness of different tick species is crucial in combating infestations effectively, particularly when concerning sensitive areas like the ear.
Symptoms of Ticks in the Ear
Understanding the symptoms of ticks in the ear is crucial for early detection and treatment. Ticks can lead to various health issues for both humans and pets. Recognizing the signs can make a significant difference in avoiding complications. Delayed identification often results in more severe health impacts, such as infections or more extensive tick-borne illness.
Common Symptoms in Humans
Itching
Itching is one of the first indicators of a tick infestation. When a tick bites, it releases chemicals that can cause a localized allergic reaction. This reaction manifests as itching, prompting individuals to scratch the affected area. The intensity of the itching can vary from mild to severe, leading to discomfort.
The key characteristic of itching is its immediate nature; it signals that something is wrong. Its inclusion as a symptom in this article is essential because it allows readers to connect a visible irritation to the potential presence of a tick. However, itching may also indicate other conditions, which can cause confusion.
Discomfort
Discomfort is another significant symptom of ticks in the ear. It may present as a feeling of fullness or pressure within the ear. Individuals may describe this sensation as annoying or distracting. Discomfort can also lead to irritation and affect daily activities.
Discomfort functions as a useful symptom because it encompasses a range of experiences. It compels individuals to seek further evaluation. This symptom, however, can be subjective, making it difficult to assess its severity. Individuals must be aware that discomfort may indicate an ongoing issue requiring attention.
Infection Signs
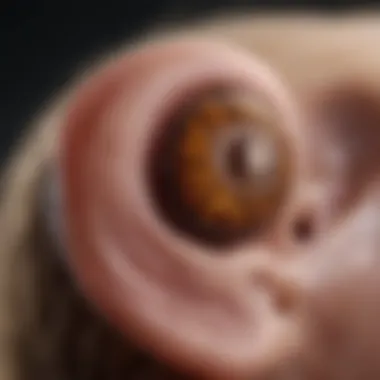

Infection signs are among the most concerning indicators of a tick infestation. Symptoms like redness, swelling, and discharge can arise as a result of a tick bite. If left untreated, these signs may point to more serious complications.
The distinctive feature of infection signs is their potential for escalation. When someone experiences these symptoms, it often indicates that medical intervention is required. In the context of this article, infection signs can alert readers to the urgency of seeking professional care. However, recognizing these symptoms can sometimes be challenging, as they may develop slowly.
Symptoms in Pets
Scratching or Shaking Head
Scratching or shaking of the head is a visible sign that pets may exhibit if they have ticks in their ears. It often indicates irritation caused by a tick bite. Pets may repeatedly try to relieve discomfort through these actions.
The primary characteristic of this symptom is its overt nature; it draws attention from owners. It plays a critical role in early detection of tick-related issues in pets. However, it's essential to recognize that frequent scratching may also be attributed to other conditions, like allergies. Owners should remain observant for additional symptoms to ensure proper evaluation.
Signs of Pain or Discomfort
Signs of pain or discomfort are often difficult to gauge in pets. Changes in behavior, such as reluctance to be touched or signs of agitation, can indicate that a pet is experiencing discomfort. The unique aspect of this symptom is its variance from one animal to another, as pets may express discomfort differently.
This symptom is critical for pet owners to understand, as it leads to timely intervention. Pets that display unusual behavior may struggle with pain that needs addressing. However, without obvious signs, some owners may overlook these indications until the situation worsens.
Unusual Behavior
Unusual behavior encompasses a range of actions. Pets may become less active, exhibit withdrawal, or show a lack of interest in play. This symptom is a broad indicator that something is off in their health.
This key characteristic allows owners to note significant behavioral changes. It can serve as an essential warning signal that professional assistance may be necessary. However, unusual behavior can stem from various causes, making it essential for pet owners to investigate underlying issues further.
Recognizing symptoms early can make a difference in treatment outcomes. Monitoring both humans and pets for these signs is essential to managing tick infestations effectively.
Risks Associated with Ticks in the Ear
Ticks can pose serious health risks to both humans and pets. Understanding these risks helps in identifying the seriousness of tick infestations. Ignoring the potential dangers can lead to severe consequences. It is essential to be informed to recognize symptoms and seek prompt treatment.
Health Risks for Humans
Lyme Disease
Lyme Disease is a well-known tick-borne illness caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. Its significance in this article is paramount due to its widespread nature and the potential for serious long-term health issues if left untreated.
The key characteristic of Lyme Disease is its long incubation period and variable symptoms. This can make it challenging to diagnose. Early signs include fever, headache, fatigue, and a distinctive skin rash known as erythema migrans. If untreated, the disease may lead to more severe complications such as arthritis, neurological issues, and heart problems. Despite these severe outcomes, treatment is often effective if initiated early, making education on prevention and recognition vital.
Hemolytic Anemia
Hemolytic Anemia is another potential consequence of tick bites. It refers to the premature destruction of red blood cells, which results in anemia. The importance of discussing Hemolytic Anemia within this context is crucial, as it can stem from the infectious agent transmitted by ticks.
A key aspect of Hemolytic Anemia is its ability to cause significant health distress. Symptoms can include fatigue, pale skin, and dark urine, reflecting the severity of blood cell destruction. The unique feature here is that this condition may arise as a reaction to certain tick-borne diseases, reinforcing the need for awareness among those who may be at risk from tick bites. Understanding this connection enables timely intervention and better overall health outcomes.
Health Risks for Pets
Canine Lyme Disease
Canine Lyme Disease, much like its human counterpart, is a disease caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. It significantly impacts dogs, often causing serious health issues if not addressed. The particularity of this disease in pets emphasizes the need for pet owners to remain vigilant and proactive.
A notable characteristic of Canine Lyme Disease is that infected dogs may not show symptoms immediately. Eventually, symptoms like lameness, fever, and swollen lymph nodes can appear. The unique feature of this disease is its potential to progress to renal complications, making prompt diagnosis and treatment crucial for recovery. Educating pet owners about this disease aids in protecting their pets’ health and wellbeing.
Tick Paralysis
Tick Paralysis is a rare but severe condition that can affect pets due to the neurotoxic effects of saliva from specific tick species. This risk is particularly important in the context of tick bites, as it can escalate quickly if not recognized.
Tick Paralysis often presents with gradual muscle weakness starting in the back legs. If not treated, it can lead to total paralysis and, in some cases, death. The unique feature here is that removing the tick usually results in a rapid improvement of symptoms. Recognizing these signs can make a significant difference, emphasizing the need for pet owners to be vigilant for tick infestations.
It is crucial to regularly check your pets for ticks and consult a veterinarian if tick-borne diseases are suspected.
Removal of Ticks from the Ear
Ticks in the ear can pose significant health risks for both humans and pets. Thus, understanding how to effectively remove them is crucial. Timely removal reduces the likelihood of infection and complications. This section outlines both self-removal techniques and professional options, equipping readers with necessary knowledge to handle tick infestations responsibly.
Self-Removal Techniques


Using Tweezers
Using tweezers is one of the most common methods for tick removal. The key characteristic of this method is its accessibility; tweezers are available in nearly every household. This approach allows for direct and careful grasping of the tick without leaving any parts behind, which is critical to prevent further complications.
The unique feature of using tweezers is the ability to apply controlled pressure. This is essential for firmly holding the tick before extraction. However, a disadvantage may arise if not executed with precision, as improper handling can lead to disease transmission. Therefore, it is vital to ensure that the tweezers grasp the tick as close to the skin's surface as possible.
Procedure for Safe Removal
The procedure for safe removal is an important aspect that underscores the need for caution and specific techniques. This procedure includes several key steps: first, ensure that you have clean hands and wear gloves if possible. Second, using tweezers, carefully grab the tick close to the skin. Third, pull upward steadily without twisting or jerking. This minimizes the risk of the tick's mouth parts breaking off and remaining embedded.
A unique feature of this procedure is its systematic approach. It emphasizes safe practices that can apply to different types of ticks. The advantages are significant; correct adherence to this process greatly reduces the risk of irritation and potential infections that arise from an improperly removed tick. However, certain individuals may feel anxious about the process, and this can impact their effectiveness during removal.
Professional Removal
When self-removal is not feasible or if there are complications, professional removal becomes a vital option. Veterinarians and healthcare providers are trained to handle tick extractions safely. They possess specialized tools and techniques to ensure thorough removal and reduce the risk of infection. In addition to extraction, they can also offer treatment options for any resulting irritation or disease.
Utilizing professional removal offers several advantages, such as reassuring experienced hands handling potentially problematic situations. Moreover, professionals can provide guidance on tick prevention and health monitoring post-removal. Overall, considering the expertise offered by professionals can significantly contribute to effective tick management.
Preventive Measures
Preventive measures are of utmost importance when dealing with ticks in the ear. Taking steps to avoid tick infestations can significantly reduce the associated health risks for both humans and pets. The following subsections outline practical strategies, emphasizing personal and pet care guidelines that can help avert tick-related issues.
Personal Care Tips
Regular Ear Checks
Regular ear checks play a critical role in maintaining ear health. By routinely inspecting the ear, individuals can identify any potential infestations early on. This practice is essential because many people may not realize when ticks have taken residence in their ears.
A key characteristic of regular ear checks is the ability to spot ticks before they cause significant discomfort. This proactive approach is beneficial, as it can prevent complications such as infections or inflammation. The unique feature of this method is its simplicity; no special equipment is needed—just a good light source and a mirror.
However, consistency is crucial. Skipping regular checks might lead to larger infestations or undiagnosed issues. Therefore, it is advisable to incorporate this routine into daily self-care practices.
Protective Gear When Outdoors
Wearing protective gear when outdoors is a practical way to reduce the risk of tick bites. This is very relevant for individuals who spend time in areas where ticks are prevalent. The key characteristic of this measure is that it acts as a barrier between the body and potential tick habitats, thus decreasing the likelihood of attachment.
Utilizing protective gear, such as long sleeves, pants, and boots, is a widely recommended choice for outdoor activities. Additionally, treating clothes with permethrin can enhance protection. The unique feature here is that these measures can help not only in preventing ticks but also other outdoor pests.
Nevertheless, there can be downsides to these precautions. Some individuals may find protective clothing uncomfortable in warmer weather, which could deter them from wearing it. Balancing comfort with safety is essential for maintaining consistent protective behaviors.
Pet Care Guidelines
Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Regular veterinary check-ups are vital for pet health, specifically in preventing tick infestations. These visits allow veterinarians to monitor pets for signs of tick-related problems and provide necessary guidance for home care. A critical aspect of these check-ups is the professional evaluation of pet's coat and skin for ticks or any abnormalities.
Regular vet visits are beneficial because they allow for timely interventions if ticks are found. The unique feature of this approach is that it creates a partnership between pet owners and professionals, fostering more comprehensive pet healthcare. Nevertheless, some pet owners may overlook the frequency of these visits, leading to gaps in preventative measures.
Tick Prevention Medications
Tick prevention medications are essential for keeping pets safe from ticks. These medications can be oral or topical, offering varying levels of protection against infestations. A key characteristic of these medications is their ability to kill ticks on contact or prevent them from attaching to the animal.
Using tick prevention medications is a popular choice among pet owners, as they actively safeguard against tick-borne diseases. The unique feature of these products is that they can provide prolonged protection, depending on the type of medication chosen. However, some pet owners might face challenges in determining which product is best suited for their specific pets, as there are numerous options available on the market.
A comprehensive approach combining personal care tips and pet care guidelines enhances protection against ticks in the ear.
Closure
The discussion surrounding ticks in the ear is critical to understanding not only their biological aspects but also the health risks they pose to both humans and pets. Addressing this topic offers several specific benefits. First, it allows readers to become informed about the nature of tick infestations. This knowledge is crucial for recognizing early signs and preventing more severe complications from developing.
Second, it underscores the importance of preventive measures. By learning techniques for personal and pet care, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of an infestation. This falls in line with broader public health objectives aimed at controlling tick populations and minimizing their impact on ecosystems.
Furthermore, the article sheds light on the role of awareness in health education. Many individuals remain unaware of ticks’ presence in areas commonly neglected, such as the ear. Increased awareness can lead to earlier detection and treatment, thereby enhancing overall health outcomes.
Finally, returning to the implications for pets elaborates on why pet owners must remain vigilant. Regular veterinary check-ups and proper knowledge regarding tick prevention medications can safeguard their pets’ health. The holistic approach detailed in the article emphasizes that understanding ticks is not merely academic. Rather, it holds practical implications for health, safety, and wellbeing.
Final Thoughts on Tick Awareness
In summary, developing awareness about ticks, especially in atypical locations like the ear, enriches the dialogue on health and safety. The information provided equips both individuals and pet owners with actionable insights to combat tick-related issues.
Awareness is the first step toward prevention. Knowledge empowers individuals to act, ensuring that ticks do not become a silent threat to health.
By fostering a proactive attitude toward tick awareness, readers will be better equipped to address the risks associated with tick infestations — for themselves and their beloved pets. The overall goal is to cultivate a society that values health education as a fundamental aspect of daily life.















